1. 概述
本文档详细描述了使用曦云® 系列GPU视频编解码VPU进行硬件加速的软件开发方法,旨在帮助开发人员利用曦云系列GPU提供的计算资源,快速构建自己的应用。
本文档主要适用于利用曦云系列GPU视频编解码VPU进行开发的软件开发人员。
2. 简介
2.1. 系统架构
曦云系列GPU视频编解码VPU的系统整体架构如下图所示:
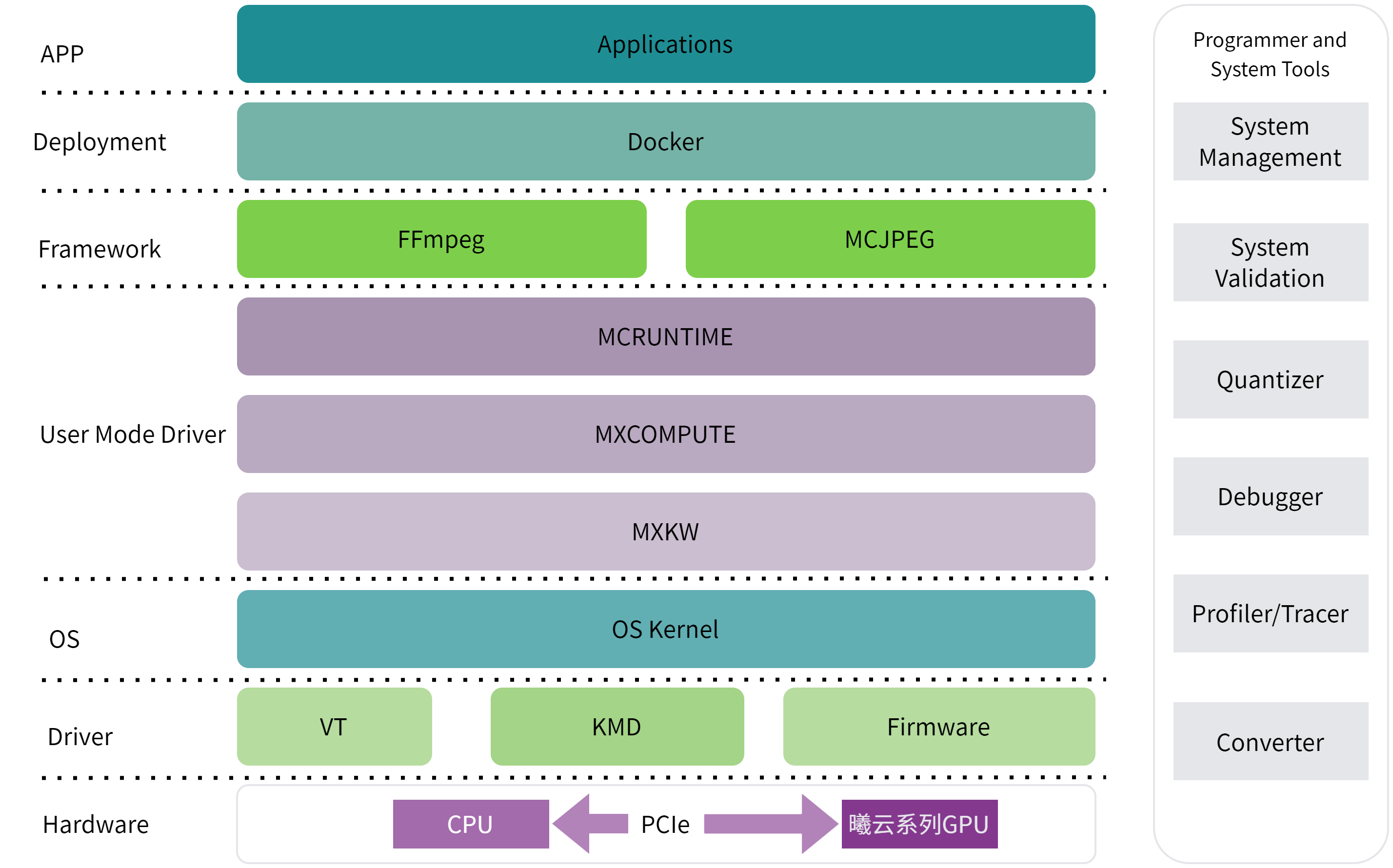
图 1 系统架构
MCRUNTIME:曦云系列GPU用户接口API,主要包括设备管理API,事件管理API,流管理API,内存管理API,模型推理API,图像处理API以及视频处理API等
MXCOMPUTE:曦云系列GPU UMD运行时API
MXKW:与曦云系列GPU驱动交互的user-mode API
3. 编程模型
3.1. 设备管理
一个服务器主机系统可以有多个设备,设备之间可以通过PCIe或者MetaXLink进行通信。曦云系列GPU提供了查询和管理设备的方法。通过这些方法,可选择合适的设备进行任务工作。
本节主要介绍方法接口,具体示例代码,参见《曦云® 系列通用计算GPU 运行时API编程指南》。
3.1.1. 查询设备信息
主机线程可以通过调用 mcGetDeviceCount() 随时查看可以使用的GPU数量,并通过调用 mcGetDeviceProperties() 查询每个设备的属性。
3.1.2. 选择运行设备
主机线程可以通过调用 mcSetDevice() 选择要执行操作的设备。在当前设置的设备上进行设备内存分配和内核启动;创建与当前设置的设备相关联的流和事件。
如果未调用 mcSetDevice() ,则当前设备为设备0。
3.1.3. 初始化设备
当主机线程调用 mcDeviceReset() 时,会破坏主机线程当前操作设备(即选择运行设备中定义的当前设备)的主要上下文。
将此设备作为当前设备的任何主机线程,进行下一次运行时函数调用时,将为此设备创建新的主要上下文。
3.2. 内存管理
曦云系列GPU内存可以分为主机系统内存(system memory)和设备内存(device memory)。
3.2.1. 内存申请与释放
申请系统内存时,使用 mcMallocHost() API。
mcMallocHost(void **ptr, size_t sizeBytes, unsignet int flags)
当需要分配设备内存时:
通过
mcSetDevice(deviceId)API选择需要分配内存的设备,若不显示指定设备,则默认分配到deviceId=0。通过
mcMalloc(void **ptr,size_t sizeBytes)API分配设备内存。使用上述接口分配出来的内存均为SVM内存,即设备和CPU均可以访问。
系统内存和设备内存的释放分别使用 mcFreeHost(void *ptr) 和 mcFree(void *ptr) 。
3.2.2. 内存拷贝
曦云系列GPU支持系统内存与设备内存之间进行拷贝,或者设备内存之间以及系统内存之间拷贝。内存拷贝分为两种类型:阻塞拷贝与异步拷贝。
阻塞拷贝与glibc提供的
memcpy类似,可以使用mcMemcpy()API,直到全部数据拷贝完成,该API才会返回。异步拷贝依赖于流,异步拷贝将拷贝任务放到流队列后,API直接返回,需要用户通过流机制查询是否执行完成。异步拷贝使用
mcMemcpyAsync()APl。
4. 视频编解码
4.1. 视频编码
4.1.1. 支持编码标准
支持以下格式视频编码:
HEVC (H.265)
Main Profile, Level 5.1, High Tier
Main 10 Profile, Level 5.1, High Tier
Main Still Picture Profile, Level 5.1, High Tier
AVC (H.264)
Baseline Profile, Levels 6.2
Main Profile, Levels 6.2
High Profile, Levels 6.2
High 10 Profile, Levels 6.2
JPEG
4.1.2. 编码流程
调用
mcInitAPI进行设备初始化。调用
mcSetDeviceAPI选择合适的设备。执行以下命令,声明一个编码器资源对象并调用
mcVpueOpenAPI初始化编码器资源。mcVPUInst encInst; mcVpueOpen(&encInst);
使用
mcVpueCtrlAPI配置编码参数。mcVpueCtrlAPI提供了丰富的控制编码器功能,使用mcSetEncAll参数携带mcVPUEncParamterType结构体来配置编码器。代码示例如下:mcVPUEncParamterType cfg; memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(mcVPUEncParamterType )); //配置清零 cfg.code_type = mcVpuH264; //配置编码标准为h264 cfg.width = 1920; //配置原始图片宽 cfg.height = 1080; //配置原始图片高 cfg.pixfmt = mcEncYuv420Planar; //配置原始图片yuv格式或rgb格式 mcVpueCtrl(encInst, mcSetEncAll, (void*)&cfg);
调用
mcVpuePutFrameAPI将原始数据发送到编码器开始编码。在MCRUNTIME中,原始数据和编码后数据都使用
mcVpuFrameInfo结构体表示。 调用时需要确保mcVpuFrameInfo结构体中的addr指针指向有效的原始数据,len等于有效的一帧数据长度。调用时,
mcVpuFrameInfo结构体中的addr指针由用户负责申请和释放。调用
mcVpueGetFrameAPI来获取编码后数据。编码后数据保存在
mcVpuFrameInfo结构体中的addr指向的内存中,长度信息在len成员中。调用mcVpueGetFrame时,mcVpuFrameInfo中的内存由编码器申请,需要用户在使用后调用mcVpueCtrlAPI携带mcFreeOutputFrame参数释放该帧内存。调用
mcVpuePutFrameAPI携带0长度的一帧输入数据,表示输入结束。调用
mcVpueGetFrameAPI,当函数返回mcSuccess且获取到0长度的输出帧时,表示编码已经结束。调用
mcVpueCloseAPI关闭编码器内部资源。
4.1.3. 编码输入内存类型
编码数据结构中,用 mcVpuMemType 枚举类型表示视频数据的存储位置和类型,具体的定义如下:
typedef enum {
mcMemHost, //存储在主机内存的数据
mcMemDevice, //存储在设备内存的数据
mcHost3Plane, //存储在主机内存且用3个地址分开存储yuv通道数据
mcDevice3Plane, //存储在设备内存且用3个地址分开存储yuv通道数据
mcMemMappedHost,//存储在主机和设备都能访问的地址的数据
} mcVpuMemType;
帧数据结构体 mcVpuFrameInfo 含有 mcVpuMemType mem_type 成员,表示当前帧数据存储和布局类型。编程时需选择正确的内存类型且使用对应的地址和长度成员变量。
当帧内存类型为以下3种时,
mcVpuFrameInfo中的addr和len分别为数据的有效地址和长度:mcMemHostmcMemDevicemcMemMappedHost
当帧内存类型为以下2种时,
mcVpuFrameInfo中的data[3]和line_size[3]分别为y/u/v通道的数据地址和数据长度:mcHost3PlanemcDevice3Plane
4.1.4. 编码高级配置
在初始化编码器后,通过调用 mcVpueCtrl API携带 mcSetEncAll 、 mcVPUEncParamterType 类型参数来配置编码器。编码器主要有以下配置项:
GoPSize:配置Group of Pictures大小通常,一个GoPSize的第一帧编码为关键帧。
rc_mode:配置码率控制模式SDK编码器支持4种码率控制模式:CBR,VBR,CRF和CQP模式。
配置CBR或VBR码率控制模式时,需要配置合适的目标码率(Bps); 配置CRF模式时即开启2 pass编码,可以同时配置
lookaheadDepth选择合适的Lookahead Frames; 配置CQP模式时,需要配置rc_val,固定QP的值即等于rc_val。qpmin qpmax:影响编码后的图片清晰度和码率大小正常编码情况下,
qpmin qpmax需要配置成0。如果需要调整QP范围,可以配置为合适的值。preset:预设编码编码器支持预设
preset为6种模式:mcEncVeryFaster,mcEncFaster,mcEncFast,mcEncMedium,mcEncSlow和mcEncSlower。ROI:每帧ROI配置,每帧图片都可以最多设置8个感兴趣区域。ROI信息保存在
mcVpuFrameInfo结构体的ROI数组内,随mcVpuePutFrameAPI的调用告知编码器。 设置ROI时需要设置mcVpuFrameInfo结构体中的roi_changed为mcTrue,并且填充ROI数组内的坐标信息和QP值。设置特定帧编码为关键帧
如果需要把某一帧原始数据编码为关键帧,只需在调用
mcVpuePutFrameAPI前,配置mcVpuFrameInfo结构体参数内的IsIDR成员为1。Bps:配置目标码率当
rc_mode配置为CBR或VBR模式时,需要设置合理的目标码率,0表示自适应。frame_order_type:配置帧顺序类型例如,配置IPB帧编码顺序类型:
0表示内部自适应;1表示第一帧为I帧,后续帧为P帧;1pass时,
2-8表示第一帧为I帧,第二帧为P帧,后续为frame_order_type-1个B帧,如此循环。
lookaheadDepth:配置前向预测深度2pass编码时,可以配置
lookaheadDepth前向预测深度。在CBR或VBR模式下,preset大于mcEncFaster,内部开启2pass编码;CRF模式下默认开启2pass编码。svc_layers:配置svc多层编码编码器支持svc多层编码,目前只开放编码层数配置,通过
svc_layers来配置编码层数。ten_bit_depth_output:控制输出帧像素深度0表示输出8-bit,1表示输出10-bit。disable_sps_pps:控制编码器是否输出SPS、PPS帧0表示输出,1表示不输出。disable_sei:控制编码器是否输出SEI帧0表示输出,1表示不输出。
4.1.5. 代码示例
示例1
基础编码,代码示例如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "mcr/mc_type.h"
#include "mcr/mc_vpu_api.h"
#include "mcr/mc_runtime_api.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
mcInit(0);
mcSetDevice(0);
mcVPUInst inst;
mcVPUEncParamterType cfg;
mcVpuFrameInfo input_frame, output_frame;
char* input_file = "demo.yuv";
char* output_file = "out.h264";
mcVpueOpen(&inst);
memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(mcVPUEncParamterType));
memset(&input_frame, 0, sizeof(mcVpuFrameInfo));
cfg.width = 320;
cfg.height = 480;
cfg.code_type = mcVpuH264;
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcSetEncAll, (void*)&cfg);
int frame_size = cfg.width * cfg.height * 3 / 2;
int infd = open(input_file, O_RDWR);
int outfd = open(output_file, O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
input_frame.addr = (uint8_t*)malloc(frame_size);
int readed, get_frame;
while((readed = read(infd, input_frame.addr, frame_size)) > 0) {
input_frame.len = readed;
mcVpuePutFrame(inst, &input_frame, NULL);
get_frame = !mcVpueGetFrame(inst, &output_frame, NULL);
if (get_frame && (output_frame.len > 0)) {
write(outfd, output_frame.addr, output_frame.len);
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void*)&output_frame);
}
}
input_frame.len = 0;
mcVpuePutFrame(inst, &input_frame, NULL);
do {
get_frame = !mcVpueGetFrame(inst, &output_frame, NULL);
if (get_frame && (output_frame.len > 0)) {
write(outfd, output_frame.addr, output_frame.len);
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void*)&output_frame);
} else if (get_frame && !output_frame.len) {
break;
} else {
usleep(100);
}
} while (1);
free(input_frame.addr);
mcVpueClose(inst);
mcDeviceDestroy();
close(infd);
close(outfd);
}
示例2
ROI编码,代码示例如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "mcr/mc_type.h"
#include "mcr/mc_vpu_api.h"
#include "mcr/mc_runtime_api.h"
void set_default_roi(mcVpuFrameInfo* frame)
{
frame->roi_changed = mcFalse;
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
frame->roi[i].roiAreaBottom = -255;
frame->roi[i].roiAreaRight = -255;
frame->roi[i].roiAreaTop = -255;
frame->roi[i].roiAreaLeft = -255;
frame->roi[i].roiQp = -1;
frame->roi[i].roiDeltaQp = 0;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
mcInit(0);
mcSetDevice(0);
mcVPUInst inst;
mcVPUEncParamterType cfg;
mcVpuFrameInfo input_frame, output_frame;
char* input_file = "demo.yuv";
char* output_file = "out.h264";
mcVpueOpen(&inst);
memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(mcVPUEncParamterType));
memset(&input_frame, 0, sizeof(mcVpuFrameInfo));
cfg.width = 320;
cfg.height = 480;
cfg.code_type = mcVpuH264;
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcSetEncAll, (void*)&cfg);
int frame_size = cfg.width * cfg.height * 3 / 2;
int infd = open(input_file, O_RDWR);
int outfd = open(output_file, O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
input_frame.addr = (uint8_t*)malloc(frame_size);
set_default_roi(&input_frame);
int readed, get_frame;
while((readed = read(infd, input_frame.addr, frame_size)) > 0) {
input_frame.len = readed;
input_frame.roi_changed = mcTrue;
input_frame.roi[1].roiAreaBottom = 60; // here you can change every frame’s roi area
input_frame.roi[1].roiAreaRight = 60;
input_frame.roi[1].roiAreaTop = 0;
input_frame.roi[1].roiAreaLeft = 0;
input_frame.roi[1].roiQp = 47;
input_frame.roi[1].roiDeltaQp = 0;
mcVpuePutFrame(inst, &input_frame, NULL);
get_frame = !mcVpueGetFrame(inst, &output_frame, NULL);
if (get_frame && (output_frame.len > 0)) {
write(outfd, output_frame.addr, output_frame.len);
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void*)&output_frame);
}
}
input_frame.len = 0;
mcVpuePutFrame(inst, &input_frame, NULL);
do {
get_frame = !mcVpueGetFrame(inst, &output_frame, NULL);
if (get_frame && (output_frame.len > 0)) {
write(outfd, output_frame.addr, output_frame.len);
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void*)&output_frame);
} else if (get_frame && !output_frame.len) {
break;
} else {
usleep(100);
}
} while (1);
free(input_frame.addr);
mcVpueClose(inst);
mcDeviceDestroy();
close(infd);
close(outfd);
}
示例3
Lookahead编码,代码示例如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "mcr/mc_type.h"
#include "mcr/mc_vpu_api.h"
#include "mcr/mc_runtime_api.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
mcInit(0);
mcSetDevice(0);
mcVPUInst inst;
mcVPUEncParamterType cfg;
mcVpuFrameInfo input_frame, output_frame;
char* input_file = "demo.yuv";
char* output_file = "out.h264";
mcVpueOpen(&inst);
memset(&cfg, 0, sizeof(mcVPUEncParamterType));
memset(&input_frame, 0, sizeof(mcVpuFrameInfo));
cfg.width = 320;
cfg.height = 480;
cfg.code_type = mcVpuH264;
cfg.preset = mcEncFast;
cfg.lookaheadDepth=10;
//mcEncFaster、mcEncFast for h264.
//mcEncFaster、mcEncFast 、mcEncMedium、mcEncSlow
//mcEncSlower for hevc.
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcSetEncAll, (void*)&cfg);
int frame_size = cfg.width * cfg.height * 3 / 2;
int infd = open(input_file, O_RDWR);
int outfd = open(output_file, O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0644);
input_frame.addr = (uint8_t*)malloc(frame_size);
input_frame.roi_changed = mcFalse;
int readed, get_frame;
while((readed = read(infd, input_frame.addr, frame_size)) > 0) {
input_frame.len = readed;
mcVpuePutFrame(inst, &input_frame, NULL);
get_frame = !mcVpueGetFrame(inst, &output_frame, NULL);
if (get_frame && (output_frame.len > 0)) {
write(outfd, output_frame.addr, output_frame.len);
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void*)&output_frame);
}
}
input_frame.len = 0;
mcVpuePutFrame(inst, &input_frame, NULL);
do {
get_frame = !mcVpueGetFrame(inst, &output_frame, NULL);
if (get_frame && (output_frame.len > 0)) {
write(outfd, output_frame.addr, output_frame.len);
mcVpueCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void*)&output_frame);
} else if (get_frame && !output_frame.len) {
break;
} else {
usleep(100);
}
} while (1);
free(input_frame.addr);
mcVpueClose(inst);
mcDeviceDestroy();
close(infd);
close(outfd);
}
4.2. 视频解码
4.2.1. 支持解码标准
支持以下格式视频解码:
HEVC (H.265)
AVC (H.264)
AV1
AVS2
JPEG
4.2.2. 解码流程
调用
mcInitAPI初始化设备。调用
mcSetDeviceAPI设置device ID。使用解码具体功能相关API,如
mcVpudOpen和mcVpudClose等。销毁设备任务记录。
全部任务完成后,调用
mcDeviceDestroy()API反初始化。
4.2.3. 解码输入内存类型
解码数据结构中,用 mcVpuMemType 枚举类型表示视频数据的存储位置和类型,具体的定义如下:
typedef enum {
mcMemHost, //存储在主机内存的数据
mcMemDevice, //存储在设备内存的数据
mcHost3Plane, //存储在主机内存且用3个地址分开存储yuv通道数据
mcDevice3Plane, //存储在设备内存且用3个地址分开存储yuv通道数据
mcMemMappedHost,//存储在主机和设备都能访问的地址的数据
} mcVpuMemType;
帧数据结构体 mcVpuFrameInfo 含有 mcVpuMemType mem_type 成员,表示当前帧数据存储和布局类型。编程时需选择正确的内存类型且使用对应的地址和长度成员变量。
当帧内存类型为以下3种时,
mcVpuFrameInfo中的addr和len分别为数据的有效地址和长度:mcMemHostmcMemDevicemcMemMappedHost
目前解码暂不支持
mcHost3Plane和mcDevice3Plane。
4.2.4. 代码示例
视频解码代码示例如下:
#include "mcr/mc_type.h"
#include "mcr/mc_vpu_api.h"
#include "mcr/mc_runtime_api.h"
mcError_t decTestCase(void *arg)
{
char file_output[256] = {0};
time_t timep;
tm *p;
int fp, fp_w;
uint8_t *packet_buffer;
uint32_t packet_size = BUFFER_SIZE;
mcVPUInst inst;
mcVpuFrameInfo frame;
mcVPUDecParameterType config;
uint32_t strm_read_len,hbm_size;
uint32_t closed_flag = 0, send_buffer_count = 0, rece_buffer_count = 0, read_flag = 0;
CaseParam *param = (CaseParam *)arg;
char *file_name = (char *)(param->file);
fp = open(file_name, O_RDONLY);
if (fp == -1) {
printf("Unable to open input file: %s\n", file_name);
return mcError;
}
if (flock(fp, LOCK_SH) < 0) {
printf("flock failed file: %s\n", file_name);
return mcError;
}
time(&timep);
p = gmtime(&timep);
sprintf(file_output, "%s.%d_%02d%02d_%02d_%02d_case%d.yuv", file_name, 1900 + p->tm_year, 1 + p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday,
8 + p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, param->case_id);
fp_w = open(file_output, O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666);
if (fp_w == -1) {
printf("Unable to open fp_w\n");
return mcError;
}
// step1: open vpu
mcVpudOpen(&inst);
// step2: config
if (NULL != strstr(file_name, "264")) {
config.code_type = mcVpuH264;
} else if (NULL != strstr(file_name, "hevc")) {
config.code_type = mcVpuHevc;
} else if (NULL != strstr(file_name, "ivf")) {
config.code_type = mcVpuAv1;
} else if (NULL != strstr(file_name, "avs")) {
config.code_type = mcVpuAvs2;
} else {
config.code_type = mcVpuJpeg;
}
printf("DEBUG PRINT ==============> code type:%d\n", config.code_type);
if (mcVpuJpeg == config.code_type) {
struct stat statbuff;
if (fstat(fp, &statbuff) < 0) {
printf("Unable to get file stat\n");
return mcError;
}
packet_size = statbuff.st_size;
packet_buffer = (uint8_t *)malloc(packet_size);
} else {
packet_buffer = (uint8_t *)malloc(packet_size);
}
config.pp_planar_flag = mcDecPpPlanarYuv420;
config.pic_num = 0;
config.output_dma_copy = mcTrue;
mcVpudCtrl(inst, mcSetDecAll, (void *)&config);
// step3: send & receive frames
while (1) {
if(!closed_flag) {
strm_read_len = read(fp, packet_buffer, packet_size);
if (strm_read_len) {
frame.addr = packet_buffer;
frame.len = strm_read_len;
frame.type = mcPacketType;
frame.mem_type = mcMemHost;
mcVpudPutFrame(inst, &frame, NULL);
} else {
// step4: ask codec to stop after finishing decoding all frames
mcVpudCtrl(inst, mcStopCodecWhenFinish, NULL);
closed_flag = 1;
}
}
do {
mcVpudGetFrame(inst, &frame, NULL);
if (frame.len > 0) {
if(read_flag == 0)
{
read_flag = 1;
mcVpudCtrl(inst, mcGetHbmSizeKbyte, &hbm_size);
}
if (config.output_dma_copy) {
if (write(fp_w, frame.addr, frame.len) == -1) {
perror("write error\n");
return mcError;
}
} else {
if (write(fp_w, frame.lu_addr, frame.lu_len) == -1 || write(fp_w, frame.ch_addr, frame.ch_len) == -1) {
perror("write error\n");
return mcError;
}
}
//need to free frame
mcVpudCtrl(inst, mcFreeOutputFrame, (void *)&frame);
printf("**************************************receive buffer_count = %d[%d]\n", rece_buffer_count++,
frame.len);
if ((0 == closed_flag) && ((rece_buffer_count >= config.pic_num) && (config.pic_num > 0))) {
printf("stop \n");
// step4: ask codec to stop after finishing decoding all frames
mcVpudCtrl(inst, mcStopCodecWhenFinish, NULL);
}
usleep(10 * 1000);
} else {
if (mcVpuTaskEnd == frame.task_status) {
goto TASK_STOP;
}
}
} while (frame.len > 0);
}
TASK_STOP:
// step5: close vpu
mcVpudClose(inst);
close(fp);
close(fp_w);
printf("decTestCase_H264 [%s] end\n", file_output);
return mcSuccess;
}
4.3. 多进程编解码
VPU编解码最高可支持128进程同时工作,使用多进程时需要设置以下环境变量:
export DYNAMIC_QUEUE_SCHEDULE=1
export QUEUE_MONITOR_TIME=100
export DYNAMIC_QUEUE_SCHEDULE_MONITOR_CYCLE=100
export DYNAMIC_QUEUE_SCHEDULE_FORCE_DESTROY=400
export DYNAMIC_QUEUE_SCHEDULE_FORCE_HOLD=0
5. 框架集成
5.1. FFmpeg
基于FFmpeg在多媒体领域的广泛应用和用户的开发需求,曦云系列GPU支持将MCRUNTIME中VPU和G2D集成到FFmpeg中,并选取FFmpeg4.3作为集成的基线。
5.1.1. FFmpeg编码流程
FFmpeg编码调用流程如下图所示:
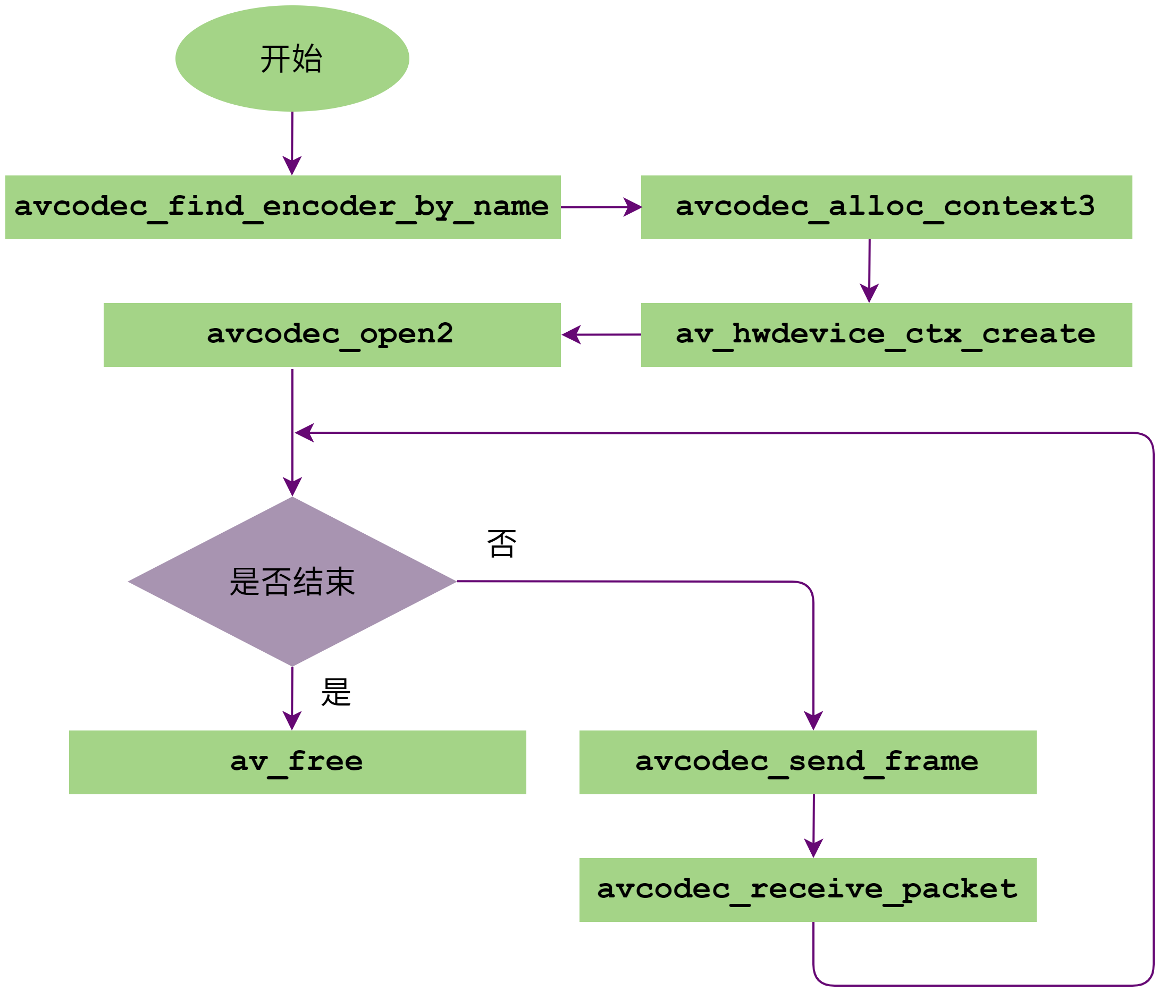
图 2 FFmpeg编码调用流程
avcodec_find_encoder_by_name:通过编码器的名称找到对应的编码器。FFmpeg支持H264、HEVC和JPEG三种编码器,分别对应名称为:h264_mxenc、hevc_mxenc和mjpeg_mxenc。用户只需要输入这些名字就可以找到对应的编码器。
avcodec_alloc_context3:获取编解码器上下文信息。av_hwdevice_ctx_create:初始化相关硬件设备,只需要输入硬件名称 mx 就可以初始化硬件设备。avcodec_open2:调用Init函数,初始化编码器。avcodec_send_frame:将需要编码的Frame数据发送到FFmpeg编码队列中。avcodec_receive_packet:从成功编码的包队列中获取一帧Packet数据。av_free:释放编码器。
5.1.2. FFmpeg解码流程
FFmpeg解码调用流程如下图所示:
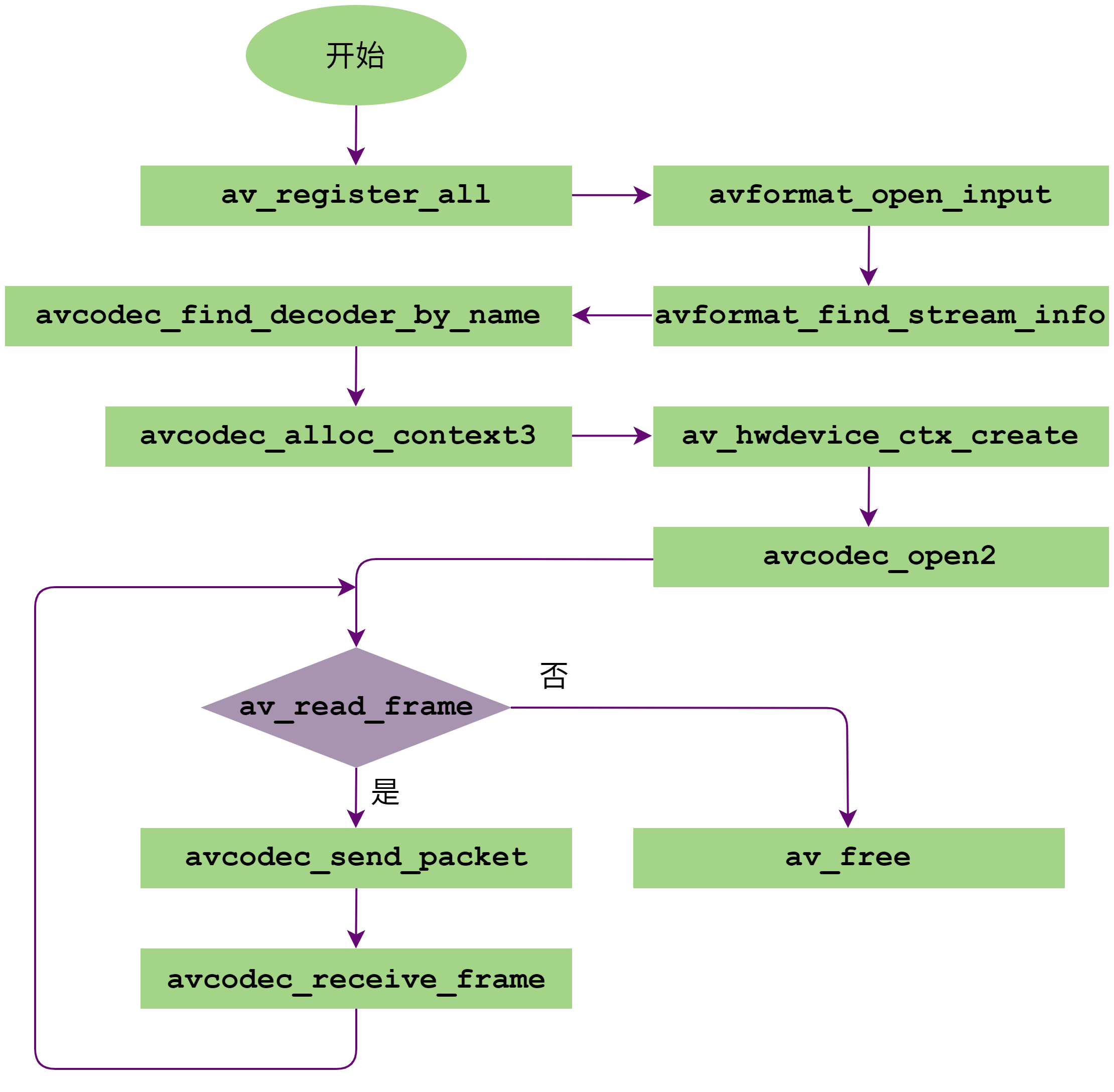
图 3 FFmpeg解码调用流程
av_register_all:注册所有codec。最新发布的FFmpeg中不需要调用此函数。avformat_open_input:初始化参数结构体,输入数据协议的识别(通过文件名后缀或读取文件头的数据进行比对)。avformat_find_stream_info:读取一些包的内容,然后从中提取流信息。avcodec_find_decoder_by_name:通过解码器的名称找到对应的解码器。FFmpeg支持H264、HEVC、AV1、AVS2和JPEG五种解码器,分别对应名称为:h264_mxvid、hevc_mxvid、av1_mxvid、avs2_mxvid和mjpeg_mxvid。下方代码示例会自动设置解码器名称,并找到对应的解码器。
avcodec_alloc_context3:获取编解码器上下文信息。av_hwdevice_ctx_create:初始化相关硬件设备,只需要输入硬件名称 mx 就可以初始化硬件设备。avcodec_open2:调用Init函数,初始化编解码。av_read_frame:获取一帧解码码流。avcodec_send_packet:发送包数据到FFmpeg解码队列中。avcodec_receive_frame:从成功解码的帧队列中获取一帧Frame数据。av_free:释放解码器。
5.1.3. 代码示例
FFmpeg解码代码如下所示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#include <libavutil/pixdesc.h>
#include <libavutil/hwcontext.h>
#include <libavutil/opt.h>
#include <libavutil/avassert.h>
#include <libavutil/imgutils.h>
static AVBufferRef *hw_device_ctx = NULL;
static enum AVPixelFormat hw_pix_fmt;
static FILE *output_file = NULL;
static int hw_decoder_init(AVCodecContext *ctx, const enum AVHWDeviceType type)
{
int err = 0;
if ((err = av_hwdevice_ctx_create(&hw_device_ctx, type, NULL, NULL, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create specified HW device.\n");
return err;
}
ctx->hw_device_ctx = av_buffer_ref(hw_device_ctx);
return err;
}
static enum AVPixelFormat get_hw_format(AVCodecContext *ctx, const enum AVPixelFormat *pix_fmts)
{
const enum AVPixelFormat *p;
for (p = pix_fmts; *p != -1; p++) {
if (*p == hw_pix_fmt)
return *p;
}
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to get HW surface format.\n");
return AV_PIX_FMT_NONE;
}
static int decode_write(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *packet)
{
AVFrame *frame = NULL, *sw_frame = NULL;
AVFrame *tmp_frame = NULL;
uint8_t *buffer = NULL;
int size;
int ret = 0;
ret = avcodec_send_packet(avctx, packet);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error during decoding\n");
return ret;
}
while (1) {
if (!(frame = av_frame_alloc()) || !(sw_frame = av_frame_alloc())) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can not alloc frame\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(avctx, frame);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) {
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_frame_free(&sw_frame);
return 0;
} else if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error while decoding\n");
goto fail;
}
if (frame->format == hw_pix_fmt) {
/* retrieve data from GPU to CPU */
if ((ret = av_hwframe_transfer_data(sw_frame, frame, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error transferring the data to system memory\n");
goto fail;
}
tmp_frame = sw_frame;
} else
tmp_frame = frame;
size = av_image_get_buffer_size(tmp_frame->format, tmp_frame->width, tmp_frame->height, 1);
buffer = av_malloc(size);
if (!buffer) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can not alloc buffer\n");
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
ret = av_image_copy_to_buffer(buffer, size, (const uint8_t * const *)tmp_frame->data,
(const int *)tmp_frame->linesize, tmp_frame->format,
tmp_frame->width, tmp_frame->height, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can not copy image to buffer\n");
goto fail;
}
if ((ret = fwrite(buffer, 1, size, output_file)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to dump raw data.\n");
goto fail;
}
fail:
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_frame_free(&sw_frame);
av_freep(&buffer);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
AVFormatContext *input_ctx = NULL;
int video_stream, ret;
AVStream *video = NULL;
AVCodecContext *decoder_ctx = NULL;
AVCodec *decoder = NULL;
AVPacket packet;
const char *hwdevice = "";
enum AVHWDeviceType type;
int i;
if (argc < 4) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <device type> <input file> <output file>\n", argv[0]);
// example: xx metax input.mp4 out.yuv xx 是程序名
return -1;
}
type = av_hwdevice_find_type_by_name(argv[1]);
if (type == AV_HWDEVICE_TYPE_NONE) {
fprintf(stderr, "Device type %s is not supported.\n", argv[1]);
fprintf(stderr, "Available device types:");
while((type = av_hwdevice_iterate_types(type)) != AV_HWDEVICE_TYPE_NONE)
fprintf(stderr, " %s", av_hwdevice_get_type_name(type));
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
return -1;
}
/* open the input file */
if (avformat_open_input(&input_ctx, argv[2], NULL, NULL) != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open input file '%s'\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
if (avformat_find_stream_info(input_ctx, NULL) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find input stream information.\n");
return -1;
}
/* find the video stream information */
ret = av_find_best_stream(input_ctx, AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, -1, -1, &decoder, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find a video stream in the input file\n");
return -1;
}
video_stream = ret;
switch (decoder->id) {
case AV_CODEC_ID_H264:
hwdevice = "h264_mxvid";
break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC:
hwdevice = "hevc_mxvid";
break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_MJPEG:
hwdevice = "mjpeg_mxvid";
break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_AVS2:
hwdevice = "avs2_mxvid";
break;
case AV_CODEC_ID_AV1:
hwdevice = "av1_mxvid";
break;
default:
break;
}
if(strlen(hwdevice)){
decoder = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(hwdevice);
fprintf(stderr, "Decoder %s find device type %s.\n", hwdevice, av_hwdevice_get_type_name(type));
}
for (i = 0;; i++) {
const AVCodecHWConfig *config = avcodec_get_hw_config(decoder, i);
if (!config) {
fprintf(stderr, "Decoder %s does not support device type %s.\n",
decoder->name, av_hwdevice_get_type_name(type));
return -1;
}
if (config->methods & AV_CODEC_HW_CONFIG_METHOD_HW_DEVICE_CTX && config->device_type == type) {
hw_pix_fmt = config->pix_fmt;
break;
}
}
if (!(decoder_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(decoder)))
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
video = input_ctx->streams[video_stream];
if (avcodec_parameters_to_context(decoder_ctx, video->codecpar) < 0)
return -1;
decoder_ctx->get_format = get_hw_format;
if (hw_decoder_init(decoder_ctx, type) < 0)
return -1;
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(decoder_ctx, decoder, NULL)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open codec for stream #%u\n", video_stream);
return -1;
}
/* open the file to dump raw data */
output_file = fopen(argv[3], "w+");
/* actual decoding and dump the raw data */
while (ret >= 0) {
if ((ret = av_read_frame(input_ctx, &packet)) < 0)
break;
if (video_stream == packet.stream_index)
ret = decode_write(decoder_ctx, &packet);
av_packet_unref(&packet);
}
/* flush the decoder */
packet.data = NULL;
packet.size = 0;
ret = decode_write(decoder_ctx, &packet);
av_packet_unref(&packet);
if (output_file)
fclose(output_file);
avcodec_free_context(&decoder_ctx);
avformat_close_input(&input_ctx);
av_buffer_unref(&hw_device_ctx);
return 0;
}
6. 附录
6.1. 调试信息
通过环境变量 VPU_LOG_LEVEL 设置日志输出等级,可选等级如下:
0:关闭日志输出
1:仅打印error级别日志
2:输出warning及error级别日志
3:输出information、warning及error级别日志
4:输出全部日志
6.2. 术语/缩略语
术语/缩略语 |
全称 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|
AV1 |
AOMedia联盟开发的视频编码标准 |
|
AVS2 |
AVS工作组制定的第二代标准 |
|
CBR |
Constant Bitrate |
恒定码率 |
CQP |
Constant Quantization Parameter |
恒定QP |
CRF |
Constant Rate Factor |
恒定码率系数 |
FFmpeg |
一款开源的多媒体数据处理框架 |
|
G2D |
Graphics2D |
图像处理单元 |
H.264 |
又称AVC,MPEG-4第十部分,视频编码标准 |
|
H.265 |
又称HEVC,MPEG-H第2部分,视频编码标准 |
|
MetaXLink |
沐曦GPU D2D接口总线 |
|
OBU |
Open Bitstream Unit |
开放比特流单元,AV1的语法结构都打包在OBU中 |
PCIe |
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express |
一种高速串行计算机扩展总线标准 |
PPS |
Picture Parameter Set |
图像参数集 |
QP |
Quantization Parameter |
量化参数 |
ROI |
Region of Interest |
感兴趣区域 |
SEI |
Supplemental Enhancement Information |
补充增强信息 |
SPS |
Sequence Parameter Set |
序列参数集 |
SVC |
Scalable Video Coding |
可分级视频编码 |
SVM |
Shared Virtual Memory |
共享虚拟内存 |
UMD |
User Mode Driver |
用户模式驱动程序 |
VPU |
Video Processing Unit |
视频处理单元 |
VBR |
Variable Bitrate |
可变码率 |